While the questions that you may be asked in a data science interview can vary a lot depending on the job description and the skillsets the organisation is looking for, there are a few questions that are often asked and as a candidate, you should know the answer to these.
Here in this post I’ll try to cover 10 such questions that you should know –
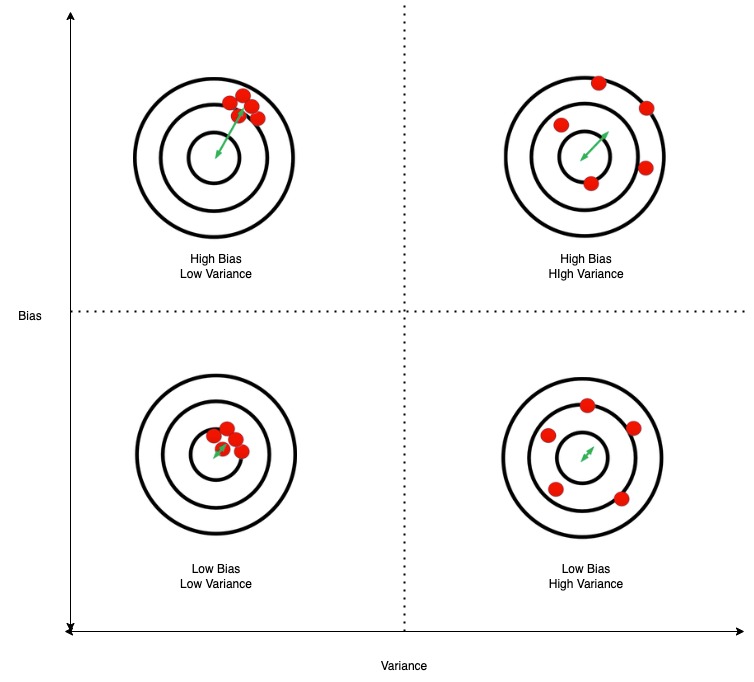
1. What is Bias-Variance Trade-off?
Bias in very simple terms is the error of your ML model. Variance is the difference in the evaluation metric in the train set and the test set that your model achieves. With any machine learning model, you try to reduce both bias and variance. The bias-variance trade-off is as you reduce bias, variance usually increases. So you try to select the ML model which has the lowest bias and variance. The below diagram should explain bias and variance.
2. In multiple linear regression if you keep adding dependent variables, the coefficient of determination (R-squared value) keeps going up, how do you then measure whether the model is improving or not?
In case of multiple linear regression, in addition to the you also calculate the adjusted r2,
, which adjusts for the number of variables in the model and penalizes models with an excessive number of variables.
You should stop adding dependent variables when the adjusted r2 values starts to worsen
3. How does Random Forest reduce variance?
The main idea behind the Random Forest algorithm is to use low-bias decision trees and aggregate their results to reduce variance. Since each tree is grown from a bagged sample and also the features are bagged, meaning that each tree is grown from a different subset of features, thus the trees are not correlated and hence their combined results lead to lower variance than a single decision tree with low bias and high variance.
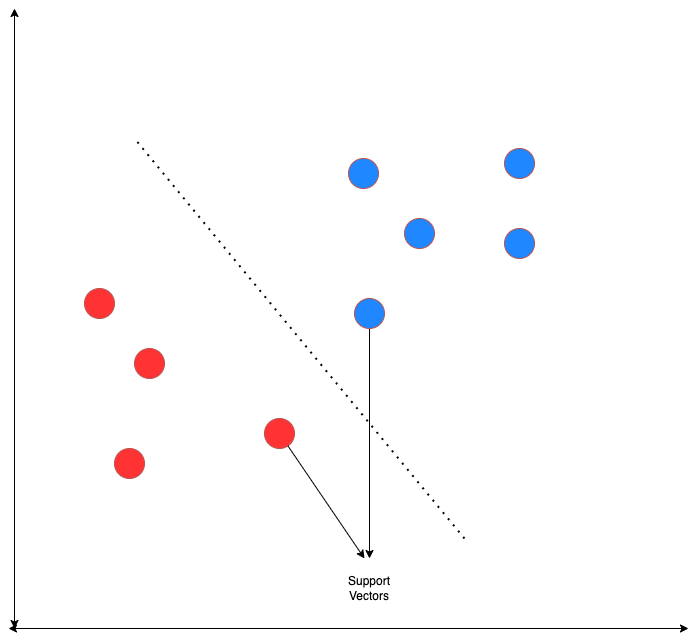
4. What are the support vectors in support vector machine (SVM)?
The support vectors are the data points that are used to define the decision boundary, or hyperplane, in an SVM. They are the key data points that determine the position of the decision boundary, and any change in these support vectors will result in a change in the decision boundary.
5. What is cross-validation and how is it used to evaluate a model’s performance?
Cross-validation involves dividing the available data into two sets: a training set and a validation set. The model is trained on the training set, and its performance is evaluated on the validation set. This process is repeated multiple times with different partitions of the data, and the performance measure is averaged across all iterations. This gives a more robust estimation of the model’s performance than a single train test split can do.
There are different types of cross-validation methods like k-fold cross-validation, in which the data is divided into k-folds, and the model is trained on k-1 folds and tested on the remaining fold. This process is repeated k times, and the performance measure is averaged across all iterations. Another one is Leave one out Cross-validation(LOOCV), in this method we use n-1 observations for training and the last one for testing. There is also a time-series cross-validation where the model is trained till time t and tested for a time after t. The window of training time keeps expanding after each iteration, it is also called expanding window cross-validation for time series.
I’ll be posting more Data Science questions on the blog so keep following for updates.